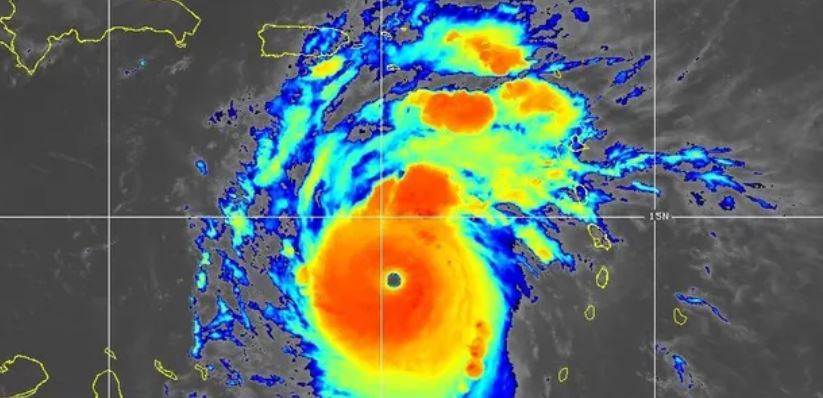
Unprecedented Hurricane Beryl Devastates Caribbean
Hurricane Beryl, the inaugural hurricane of the Atlantic in 2024, has left an indelible mark with its unparalleled intensity. This tempest, brewing in late June, unleashed its wrath on Grenada and other Windward Islands, before spiraling towards Jamaica and Mexico’s Yucatán peninsula. Beryl’s record-breaking trajectory underscores a year already replete with extreme climate events.
Record-Smashing Intensity
On June 30, Beryl became the earliest Atlantic hurricane to attain Category 4 status. Remarkably, it escalated further the very next day, becoming the earliest storm to achieve Category 5, with winds reaching an astonishing 270 kilometers per hour. Although it has slightly weakened, it remains a formidable Category 4 storm as it approaches Jamaica.
The Role of Superheated Waters
The superheated waters of the North Atlantic Ocean have fueled Beryl’s unprecedented ferocity. Scientists anticipated a “hyperactive” Atlantic hurricane season in 2024, driven by these anomalously warm waters and the imminent La Niña phase of the El Niño-Southern Oscillation (ENSO) climate pattern.
Meteorological Marvel
Brian McNoldy, an atmospheric scientist at the University of Miami, expressed astonishment at Beryl’s rapid intensification, highlighted by stunning satellite imagery. The early onset of extreme oceanic heat has contributed significantly to this phenomenon, with temperatures resembling those typically seen at the peak of hurricane season.
Ocean Heat Content: A Deeper Understanding
Understanding ocean heat content is crucial for grasping the dynamics of hurricanes like Beryl. While sea surface temperature refers to the warmth at the ocean’s surface, ocean heat content measures how deep that warmth extends. This year, the tropical Atlantic’s heat content is at an all-time high, resembling conditions usually observed in mid-September.
The Main Development Region’s Heat
The North Atlantic’s main development region, a breeding ground for hurricanes, has been primed with unprecedented warmth. This area’s ocean heat content has surpassed previous records, including those set in 2023. The sustained heat at significant depths has provided a rich energy source for Beryl’s intensification.
Implications of Deep Ocean Heat
The depth of warm water plays a critical role in a hurricane’s development. Shallow warm layers can be churned up by the storm, bringing cooler water to the surface and weakening the hurricane. However, Beryl’s environment features warm water extending down to 100-125 meters, ensuring a continuous energy supply and maintaining the storm’s strength.
Comparing Climate Patterns
While 2023 also saw record-breaking heat, the concurrent onset of a strong El Niño mitigated hurricane activity in the Atlantic by increasing wind shear. This year, the dissipated El Niño has given way to neutral ENSO conditions, with an impending La Niña expected to enhance hurricane activity by reducing wind shear, creating an optimal environment for powerful storms.
Forecasts and Future Concerns
This year’s dire hurricane forecasts stem from these unique climatic conditions. Although each year’s specific conditions vary, the overarching trend of warming oceans portends more frequent and intense hurricanes. As global temperatures rise, the likelihood of returning to previous climatic norms diminishes, highlighting an evolving and increasingly hazardous climate landscape.
Conclusion
Hurricane Beryl’s record-breaking fury exemplifies the escalating dangers posed by climate change. As the earliest Category 5 storm in Atlantic history, its devastating impact on the Caribbean underscores the urgent need for enhanced preparedness and adaptation strategies. The relentless march of global warming demands immediate and robust action to mitigate future climatic catastrophes.
Summary Table:
| Key Learning Points | Details |
|---|---|
| Hurricane Beryl’s unprecedented intensity | Earliest Atlantic storm to reach Category 5 |
| Role of superheated waters | Anomalously warm North Atlantic Ocean fuels storm |
| Ocean heat content significance | Measures depth of warm water, critical for hurricane strength |
| Main development region’s record heat | Unprecedented ocean heat content primed powerful storms |
| Climate patterns comparison | El Niño’s dissipating effect in 2023 vs. La Niña’s enhancement in 2024 |
| Future forecasts and concerns | Rising global temperatures likely to increase hurricane intensity and frequency |

Sunil Garnayak is an expert in Indian news with extensive knowledge of the nation’s political, social, and economic landscape and international relations. With years of experience in journalism, Sunil delivers in-depth analysis and accurate reporting that keeps readers informed about the latest developments in India. His commitment to factual accuracy and nuanced storytelling ensures that his articles provide valuable insights into the country’s most pressing issues.