Unprecedented Oceanic Heatwave: A Global Crisis
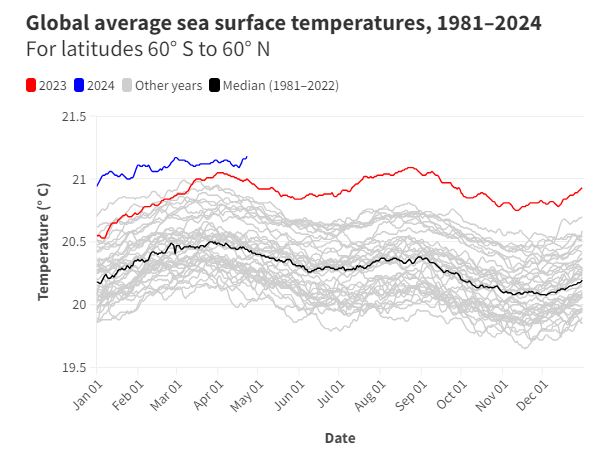
The world’s oceans are experiencing an unprecedented heatwave, with global sea surface temperatures shattering daily records for over a year. This alarming trend, exacerbated by the natural climate phenomenon El Niño and decades of escalating heat accumulation, is wreaking havoc on marine ecosystems and triggering a cascade of devastating consequences.
El Niño and the Anthropocene: A Dangerous Confluence
While El Niño, a recurring climate pattern characterized by warm surface waters in the tropical Pacific Ocean, plays a role in the current heatwave, it is crucial to recognize the underlying driver: anthropogenic climate change. The ocean has absorbed a staggering 90% of the excess heat trapped by greenhouse gases since 1971, accumulating an estimated 380 zettajoules of energy. This colossal amount of heat is equivalent to 1.5 million times the energy released by the Hunga Tonga-Hunga Ha’apai volcanic eruption in 2022, or 25 billion times the energy unleashed by the atomic bomb dropped on Hiroshima.
Consequences of a Feverish Ocean
The consequences of this oceanic fever are far-reaching and dire. A hyperactive Atlantic hurricane season looms, fueled by abnormally high sea surface temperatures in the main development region. Corals, vital ecosystems that support a quarter of all known marine species, are succumbing to mass bleaching events, expelling their symbiotic algae and revealing their skeletal remains. Meanwhile, Antarctic sea ice, a critical component of the global climate system, is experiencing alarming declines, reaching record lows for both minimum and maximum extents.
A Bleak Outlook: The Future of Our Oceans
Scientists remain uncertain about when this relentless onslaught of record-breaking sea surface temperatures will abate. While the emergence of La Niña, El Niño’s cooler counterpart, may offer some respite, previous La Niña events have not prevented record-breaking temperatures elsewhere. The stark reality is that the oceans are in crisis, and urgent action is required to mitigate the catastrophic consequences of climate change.
Key Learning Points:
| Key Point | Description |
|---|---|
| Global sea surface temperatures have been breaking daily records for over a year. | This unprecedented heatwave is driven by El Niño and decades of escalating heat accumulation due to climate change. |
| The ocean has absorbed a massive amount of excess heat. | The ocean has absorbed 90% of the excess heat trapped by greenhouse gases since 1971. |
| The consequences of this heatwave are far-reaching and dire. | These consequences include a hyperactive hurricane season, mass coral bleaching, and declining Antarctic sea ice. |
| Scientists are uncertain when this trend will abate. | While La Niña may offer some respite, previous events have not prevented record-breaking temperatures elsewhere. |

Basant Kumar Sahoo is a seasoned writer with extensive experience in crafting tech-related articles, insightful editorials, and engaging sports content. With a deep understanding of technology trends, a knack for thought-provoking commentary, and a passion for sports, Basant brings a unique blend of expertise and creativity to his writing. His work is known for its clarity, depth, and ability to connect with readers across diverse topics.



